Arduino has rolled out a new Bluetooth-based configuration process within its Arduino Cloud platform, with the UNO R4 WiFi being the first supported board. This feature significantly simplifies the initial setup steps, making the process faster, cable-free, and more user-friendly for IoT and connected projects.
Using the Arduino IoT Cloud Remote app (available for Android and iOS), users can power up the board and have it automatically detected by the app. From there, the app guides them through WiFi network setup and provides visual feedback on progress and results. Once configured, the board can be fully managed via Arduino Cloud—enabling remote monitoring, over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates, real-time dashboards, AI-powered assistance, and third-party service integrations.
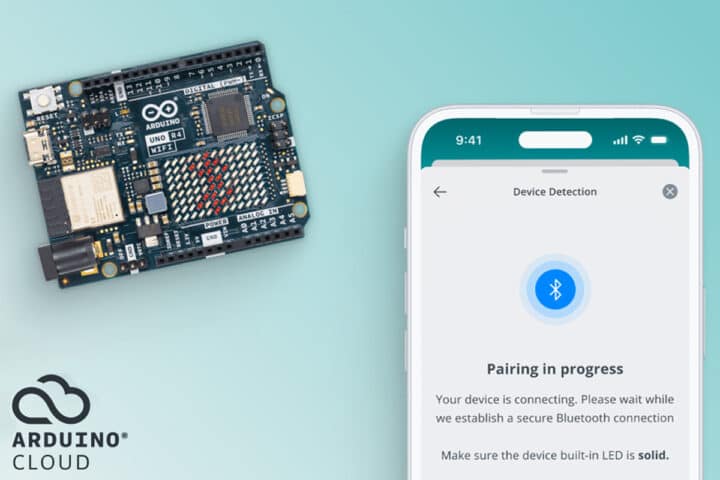
Currently, this streamlined configuration is exclusive to the UNO R4 WiFi. Buyers of this board also receive a complimentary 3-month Arduino Cloud Maker subscription, unlocking the platform’s advanced features. Arduino has confirmed that broader board support will arrive through future system updates.
Core Details of Arduino’s New Configuration Process
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Supported Boards | Initially limited to the latest stock of Arduino UNO R4 WiFi, with more models planned |
| Setup Method | Bluetooth configuration via the Arduino IoT Cloud Remote app (Android/iOS) |
| Security | Secure registration of Arduino boards with the Arduino Cloud platform |
| Cloud Integration | Seamless connection to the Arduino IoT Cloud ecosystem |
| Subscription Bundle | Includes a 3-month Arduino Cloud Maker plan at no extra cost |
| Key Advantage | Replaces captive portals or manual firmware edits with a faster, out-of-the-box setup |

Why This Matters in IoT
For IoT devices, initial setup is often the biggest pain point. While a developer might hardcode WiFi credentials directly into firmware for personal use, this approach breaks down when devices need to be deployed to end users. The industry has long needed a solution that eliminates manual code editing or flashing while still ensuring a smooth network connection. Arduino’s Bluetooth configuration directly addresses this challenge.
How It Differs from Captive Portals
Many WiFi development boards rely on a captive portal approach: the board launches a temporary hotspot, users connect to it, and then enter WiFi details before switching back to their target network.
In contrast, Arduino’s Bluetooth method is simpler. Power on the board, open the Arduino IoT Cloud Remote app, pair over Bluetooth, and select the target WiFi. Setup is complete in just a few steps.
For a deeper dive, Arduino provides official documentation that covers step-by-step guides, differences between version 1.0 and 2.0 of the setup process, supported board lists, Bluetooth vs. USB workflows, migration instructions, and methods for resetting or deleting stored credentials.

Getting Started
To try the new process, you’ll need:
- An Arduino UNO R4 WiFi board
- The Arduino IoT Cloud Remote app (available in the Google Play Store and Apple App Store for iOS and iPadOS)
Additional details and updates are available in Arduino’s official press release.