The Raspberry-Pi-powered open-source Mars Rover is a compact, DIY-friendly interpretation of NASA JPL’s rover architecture. Designed for students, hobbyists, and makers, this fully open project uses common off-the-shelf (COTS) components to replicate the core mechanical principles of a planetary exploration rover.
It offers excellent affordability, modularity, and extensibility—making it an ideal educational platform for mechanical engineering, electronics, and robotics programming.

| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Wheel Configuration | 6-wheel drive, all-terrain capable |
| Suspension System | Rocker-Bogie suspension ensuring continuous ground contact |
| Steering System | 6-wheel Ackermann-style steering with tight-radius and near-pivot turns |
| Control Core | Raspberry Pi (compatible with Pi 3, Pi 4, and Zero series), supporting multiple OS environments |
| Auxiliary Control Module | Arduino-Shield expansion board compatible with the Arduino ecosystem |
| Communication Interfaces | 4× USB ports (3 available when using an Xbox controller), I2C bus, 2× SPI buses, 3.5 mm audio jack |
| GPIO Pins | 13 GPIOs (6 remaining when an LED matrix display is connected) |
| Hardware Expansion Support | Camera port, auxiliary power connector for external peripherals |
| Open-Source Design | Onshape 3D models, SolidWorks core components, full assembly diagrams and PCB files |
| License | Apache-2.0 (supports modification and open distribution) |
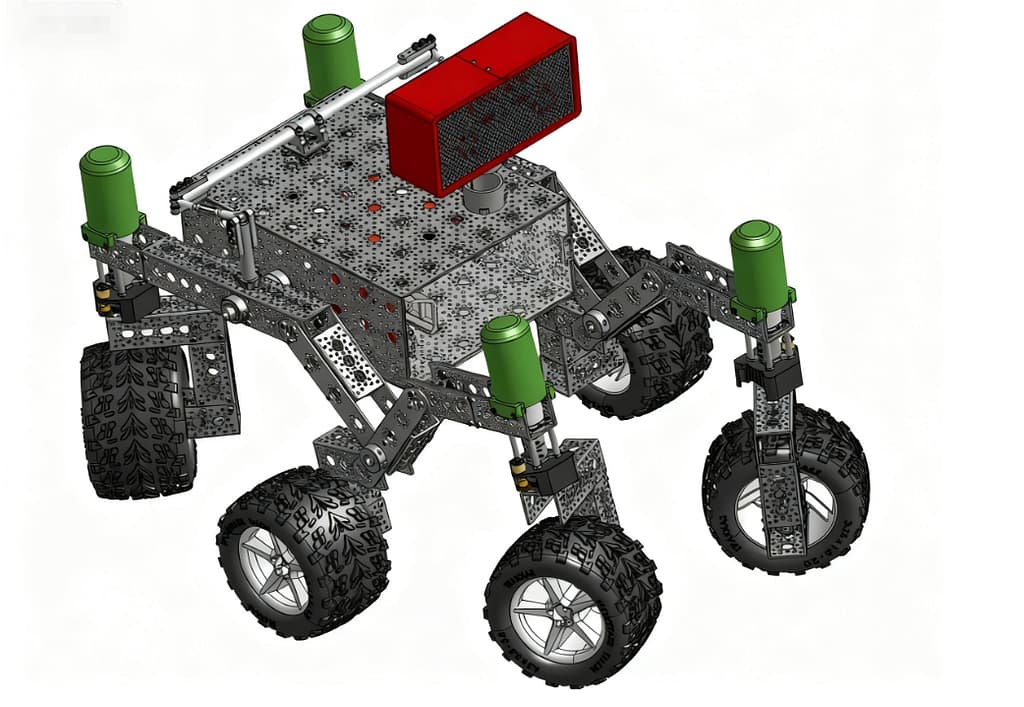
This open-source rover closely mirrors the mechanical framework of NASA’s exploration vehicles and is engineered for demanding terrain scenarios:
- Rocker-Bogie Suspension
The classic rocker-bogie architecture allows all six wheels to maintain ground contact—even over rocks, gaps, and uneven surfaces—reducing slippage and improving off-road reliability. - Mechanical Differential Pivot
During steep climbs, the pivot system helps distribute load across both sides of the chassis, reducing wheel overload and maintaining stability. It handles slopes around ~30° under appropriate gearing and motor torque. - Six-Wheel Ackermann Steering
Integrates coordinated driving and steering control, enabling smooth straight-line motion, precise cornering, and efficient operation in confined environments.
Because the rover covers mechanical assembly, electronics integration, and embedded programming, it functions as a complete teaching tool suitable for university robotics labs, K-12 STEM programs, and individual maker projects.

Recommended BOM-Based Robot Assembly
Raspberry Pi as the Control Core: A Highly Extensible “Smart Brain”
Using Raspberry Pi as the primary controller brings extensive benefits in connectivity, flexibility, and computing capability:
- Supports Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and USB interfaces—compatible with wireless controllers, mobile apps, or remote PC operation.
- Provides direct integration with Raspberry Pi Camera modules (for live video), infrared distance sensors (for autonomous obstacle avoidance), accelerometers (for attitude sensing), USB microphones (for voice interaction), and other accessories.
- Compatible with Python, C++, and various robotics frameworks. Beginners can start with simple motor control, while advanced users can implement autonomous navigation, SLAM, and path-planning algorithms.
The dedicated auxiliary power connector allows clean, separated power delivery to external modules without complex rewiring.

To broaden application scenarios, the following components integrate seamlessly with the rover platform:
- GoBilda High-Torque Motors — Provide significantly higher torque than standard DC motors, improving load capacity and slope-climbing performance in rugged terrain.
- 1080p Raspberry Pi Camera Module — Enables real-time video streaming and computer vision tasks such as object detection and environmental mapping.
- Bluetooth 5.0 Game Controller — Offers wireless control up to ~10 m with customizable input mapping for intuitive operation.
- 12 V Rechargeable Li-ion Battery Pack — 2000 mAh capacity with up to ~4 hours of operation depending on load and usage profile.
- Infrared Distance Sensor — 0–80 cm detection range, ideal for entry-level obstacle-avoidance programming.
- LED Status Display — Shows battery level, communication status, and system indicators for quick diagnostics.
Open-Source Resources and Assembly Support
1. Online 3D Model Reference
The project provides a complete Onshape online 3D model with step-by-step assembly views. A detailed illustrated guide supports beginners in following the mechanical build process.
Note: The SolidWorks files represent the most up-to-date and authoritative version, while Onshape models may occasionally lag behind.

Rover Assembly Stages
2. Phased Assembly Guide
The build process is divided into three primary stages:
- Mechanical chassis assembly
- Electronic module soldering and integration
- Control-board configuration and calibration
Each stage includes clear schematics and real-world photos, and the design supports 3D-printed components for non-standard or custom parts.

3. Hardware Design Resources
- Control Board: Complete PCB design files and soldering diagrams for fabrication or customization.
- Arduino-Shield Expansion Board: Compatible with Arduino Uno/Nano and supports sensors, relays, and extended electronic modules.
- Port-Mapping Diagrams: Detailed interface definitions help prevent wiring mistakes and reduce debugging complexity.
Open-Source Licensing and Secondary Development
The project is released under the Apache-2.0 license, granting individuals, educators, and research teams the freedom to use, modify, and redistribute the design without licensing fees.
The repository and downloads are available on GitHub through the open-source project: