Qualcomm Technologies has officially announced its plan to acquire Arduino, marking a pivotal moment for both the embedded systems industry and the maker community. The goal behind this acquisition is to combine Qualcomm’s expertise in edge computing and artificial intelligence (AI) with Arduino’s massive global developer ecosystem and its open-hardware philosophy, creating a stronger, more competitive technology landscape.
Alongside the acquisition announcement, two flagship products were unveiled:
- Arduino UNO Q – a dual-processor development board built around Qualcomm’s Dragonwing QRB2210 platform.
- Arduino App Lab – a cross-platform development environment designed to unify Linux, RTOS, Python, and AI workflows under one roof.
This move follows Qualcomm’s earlier integrations of Edge Impulse and Foundries.io, strengthening its strategy to deliver a complete “hardware-to-cloud” stack for edge developers.
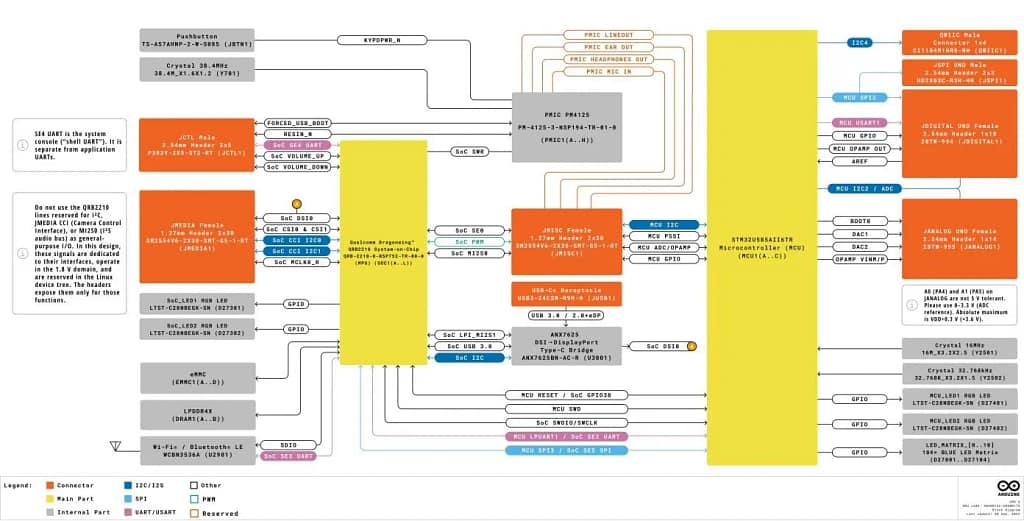
Arduino UNO Q Block Diagram
Arduino confirmed that even after the acquisition, it will remain an independent brand committed to its open-source mission. At the same time, it will join Qualcomm’s global ecosystem and benefit from advanced technologies that accelerate its growth.
With over 33 million active users, the Arduino community stands to gain directly from this partnership. Developers will have access to enhanced prototyping and commercialization tools. Importantly, Arduino will continue to support hardware from multiple semiconductor vendors, ensuring the platform remains open and interoperable.
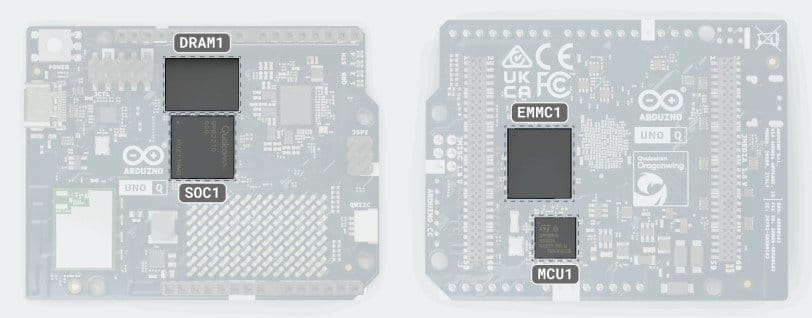
Arduino UNO Q Processing and Memory Architecture
The launch of the Arduino UNO Q signals a major evolution: development boards shifting from a single microcontroller design toward a hybrid architecture of high-performance computing + real-time control.
The board integrates two processors:
- Qualcomm Dragonwing QRB2210 – a quad-core Arm Cortex-A53 SoC with GPU and AI acceleration, capable of running full Linux environments.
- STMicroelectronics STM32U585 – an Arm Cortex-M33 microcontroller optimized for deterministic, real-time tasks.
This combination allows developers to target projects that need both deterministic control and on-device machine learning inference, such as smart home devices, robotics platforms, and industrial automation systems.
The UNO Q retains compatibility with existing Arduino shields and follows the familiar UNO form factor, lowering adoption barriers. It also introduces high-speed peripheral interfaces for cameras, displays, and advanced sensors. On the software side, the MPU runs Debian Linux, while the MCU executes an RTOS. Developers can work within a unified environment where complex applications and low-latency tasks run in parallel—streamlining the development process.
Beyond hardware, Arduino introduced App Lab, a unified development environment designed to simplify multi-domain programming.
App Lab integrates seamlessly with Edge Impulse, enabling model training and optimization directly within the workflow. Developers can quickly build AI-driven applications like object detection, sound recognition, and anomaly detection using real-world data. The environment also provides prebuilt Arduino Apps and Bricks for faster prototyping and deployment.
Nakul Duggal, GM of Qualcomm’s Automotive, Industrial, and Embedded IoT division, emphasized that acquiring Arduino aligns with Qualcomm’s mission of making advanced computing more accessible, expanding its reach across industries.
Fabio Violante, CEO of Arduino, noted that the collaboration will greatly improve accessibility while accelerating innovation. Arduino co-founder Massimo Banzi added that the company remains firmly committed to its open-source values, ensuring the community continues to thrive.
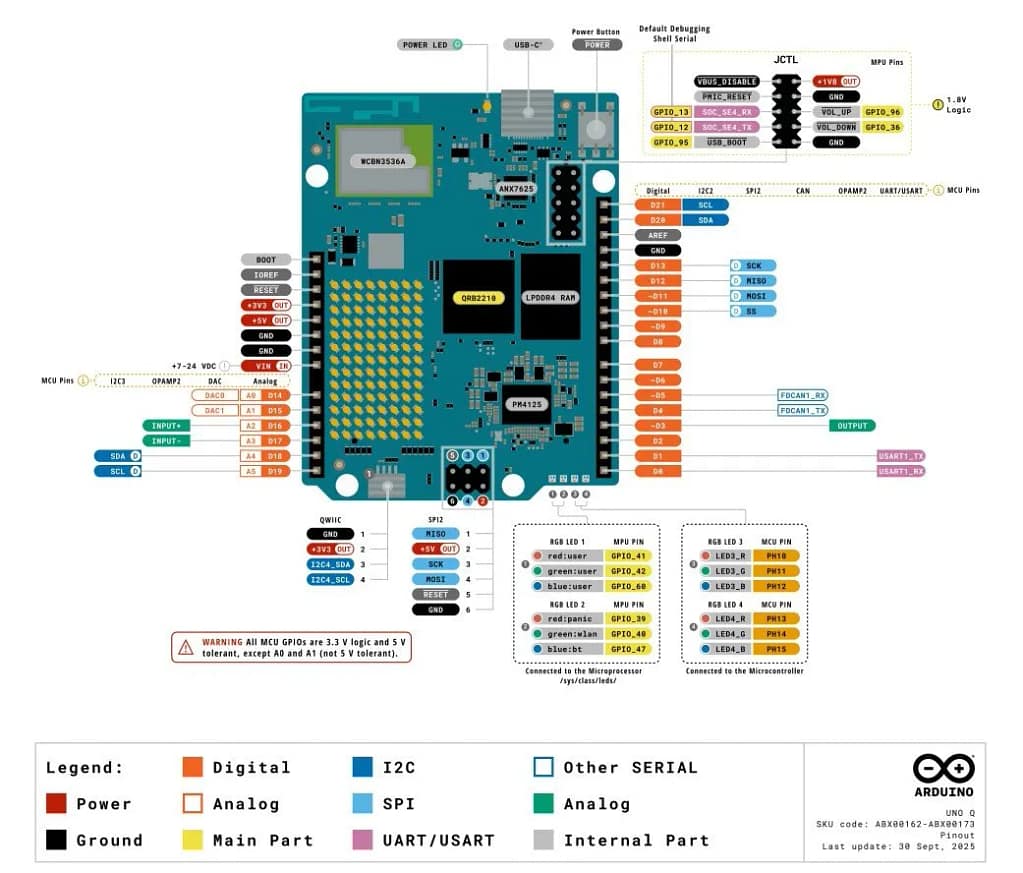
Arduino UNO Q Specifications
Microprocessor (MPU):
- Qualcomm Dragonwing QRB2210, quad-core Arm Cortex-A53, up to 2.0 GHz
- Integrated Adreno GPU for 3D graphics acceleration
- Dual ISP supporting dual 13 MP cameras or a single 25 MP camera (30 fps)
Microcontroller (MCU):
- STMicroelectronics STM32U585, Arm Cortex-M33 up to 160 MHz
- 2 MB Flash, 786 KB SRAM
Memory:
- 2 GB LPDDR4 RAM
Storage:
- 16 GB eMMC
Connectivity:
- Wi-Fi 5 (2.4/5 GHz) with onboard antenna
- Bluetooth 5.1 with onboard antenna
Interfaces:
- I²C / I³C, SPI, UART, PSSI
- PWM, CAN, GPIO
- JTAG, ADC
Video:
- USB-C video output
- JMEDIA MIPI DSI interface for displays
Audio:
- JMISC interface for mic input, headphone out, and line out
USB:
- One USB-C port (host/device role swap, power role swap, video out)
Additional Features:
- 4 user-programmable RGB LEDs
- 8×13 blue LED matrix
- Qwiic connector (3.3 V I²C)
- JCTL connector for MPU remote debugging
- 1 user button
Power Supply:
- 5 V DC via USB-C, up to 3 A
Dimensions:
- 68.85 × 53.34 mm (standard UNO form factor)
Operating Systems:
- MPU: Debian Linux
- MCU: Arduino Core with Zephyr RTOS
Containerization:
- Supports Docker and Docker Compose
App Lab Host OS Support:
- Windows 10+ (64-bit)
- macOS 11+ (64-bit)
- Linux Ubuntu 22.04+, Debian Trixie (64-bit)
The Arduino UNO Q is now available for pre-order on the official Arduino store at €47.60, with shipping starting October 24. Distribution will later expand through RS Components, Digi-Key, Mouser, Macfos, and other global distributors.
More technical details and live demonstrations will be shared in Arduino’s upcoming event “From Blink to Think”, where developers can explore real-world use cases of the UNO Q.